Die Wahl zwischen einem Bluetooth LE-Modul und einem System-on-Chip (SoC) ist eine wichtige, aber auch anspruchsvolle Entscheidung beim Design von Bluetooth- Geräten. Jede Option bietet ihre eigenen Vor- und Nachteile, sodass Leistung, Funktionen und Kosten sorgfältig abgewogen werden müssen.
Als erfahrener Experte für Bluetooth-Technologie möchte RF - star den Entscheidungsprozess vereinfachen , indem es einen detaillierten Vergleich von Bluetooth-Chipsätzen und -Modulen bereitstellt . Dieser Leitfaden hilft Ihnen, basierend auf Ihren Produktionsmengen , Ihrem technischen Know-how , Ihrem Budget und Ihrer Markteinführungszeit die beste Wahl zu treffen .
Ein Bluetooth System-on-Chip (SoC) ist ein integrierter Schaltkreis (IC) , der die Bluetooth-Kommunikation innerhalb eines Geräts ermöglicht . Er umfasst normalerweise einen Kernprozessor, einen HF-Transceiver, Speicher und Zusatzschaltkreise. Der SoC dient als Herzstück der Bluetooth-Kommunikation und verwaltet die Datenübertragung und -verarbeitung.
Im Gegensatz dazu ist ein Bluetooth LE- Modul eine vorzertifizierte Einheit, die als umfassende und stromsparende Bluetooth- Kommunikationslösung fungiert . Es integriert ein Bluetooth LE SoC mit zusätzlichen Komponenten wie HF-Schaltkreisen, Quarzoszillatoren, Antennenanpassungsschaltungen, Antennen, Balun und Peripherieschnittstellen auf einer Leiterplatte ( PCB ) . Das Modul ist eine vorkonfigurierte Plug-and-Play-Lösung, die die Produktentwicklung erheblich vereinfacht und es Entwicklern ermöglicht, sich auf höherwertige Produktfunktionen zu konzentrieren, ohne sich um das zugrunde liegende HF-Design kümmern zu müssen.

TI CC2340 SoC & RF-star RF-BM-2340B1 Modulbeispiele
Wir verwenden die folgenden Schlüsselmetriken , um die Unterschiede zwischen Bluetooth LE- Modul und SoC zu vergleichen:
Ein Bluetooth-SoC bietet die wesentlichen Funktionen für die Bluetooth-Kommunikation, erfordert jedoch zusätzliche Peripheriekomponenten, um ein voll funktionsfähiges System zu erstellen. Entwickler, die sich für ein SoC entscheiden , müssen die erforderlichen HF-Schaltkreise, das Energiemanagement und die eingebettete Software entwerfen und implementieren.
This level of customization is beneficial in situations when the product’s form factor, power consumption, and performance must be finely tuned. However, it also means that the development cycle will be longer, and the project may require a team with specialized expertise in RF design and embedded software development.
Conversely, Bluetooth modules come with integrated peripheral RF circuitry and relevant embedded software, such as Bluetooth 5.0 serial port firmware, UART direct-driven firmware, SPI transparent transmission firmware, and I2C firmware. Developers can use an external MCU to control the Bluetooth connectivity directly, significantly reducing both the workload and complexity of product development. It allows developers to focus on the application layer and integrate Bluetooth connectivity into their products more quickly.
If you know more Bluetooth serial port modules, check the blog Generic Serial Communication Protocols: UART, SPI, I2C.
Bluetooth Low Energy modules are designed with user-friendliness in mind. They often feature standardized hardware interfaces — such as UART, SPI, I2C, and GPIOs — and software protocols, making them easy to integrate into a variety of systems.
Additionally, Bluetooth LE modules typically come with extensive documentation, development kits, and reference designs, further easing the development process. Many modules are also accompanied by robust software stacks that provide essential Bluetooth profiles and services out of the box. This means that even developers with limited Bluetooth experience to successfully integrate wireless connectivity into their products.
In contrast, using a Bluetooth SoC demands greater technical expertise. The development team must be proficient in RF hardware and embedded software design. This involves creating RF circuitry, selecting and placing components, optimizing power, and ensuring Bluetooth compliance. While this approach offers flexibility and potential cost savings in high-volume production, it requires more time, resources, and specialized knowledge.
The choice between a Bluetooth LE SoC and a module largely depends on the application. Bluetooth modules are ideal for implementing wireless connectivity with minimal effort, especially in moderate production volumes where convenience and shorter development times outweigh the higher unit cost.
Common applications for Bluetooth LE modules include smart home devices, such as smart plugs, light bulbs, and security cameras; smart medical devices, such as blood glucose monitors and digital thermometers; and industrial IoT devices, such as sensors and actuators that require reliable wireless communication.
Bluetooth SoCs, however, are better suited for applications that require high customization, integration, and scalability. They are often used in large production volumes, where cost savings from using SoCs are substantial.
Typical applications include high-performance consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops; wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers; and automotive applications, such as in-car entertainment systems and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Cost is often a decisive factor in choosing between a Bluetooth SoC and a module. Bluetooth modules with pre-certified RF circuitry, an antenna, and a software stack may raise the cost of buying one. Its initial purchase cost sounds higher than SoC’s.
However, this higher cost should be weighed against the potential savings in development time and resources. When using a Bluetooth SoC, the following development-related expenses should be taken into consideration:
While SoC might have a lower initial cost, it can incur additional expenses during development.
For large-scale production, however, the higher upfront investment in development can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. According to an analysis by Silicon Labs, SoCs may offer a cost advantage over modules when annual production volumes exceed 500,000 to 1.3 million units. This makes SoCs an attractive option for high-volume products where reducing the bill of materials (BOM) cost is critical to maintaining profitability.
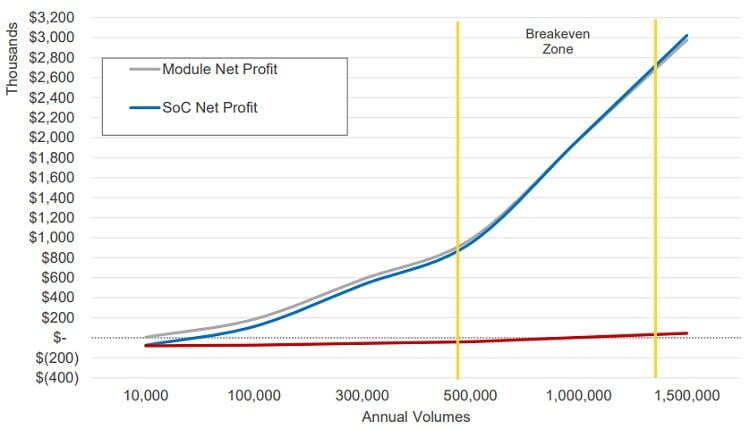
Break-even for a wireless SoC and wireless module. Source from Silicon Labs
Supply chain management is another crucial consideration when choosing between a Bluetooth chipset and a module.
With a Bluetooth LE module, you only need to manage the module vendor, who is responsible for ensuring the module's quality, availability, and compliance with industry standards.
Beim SoC-basierten Design müssen Sie jedoch mehrere Lieferanten verwalten, darunter den SoC-Anbieter, den PCB-Hersteller, den Antennenlieferanten und möglicherweise noch weitere. Jeder dieser Lieferanten kann unterschiedliche Lieferzeiten, Produktlebenszyklen und Qualitätskontrollprozesse haben, was das Lieferkettenmanagement komplexer macht und mehr Ressourcen erfordert.
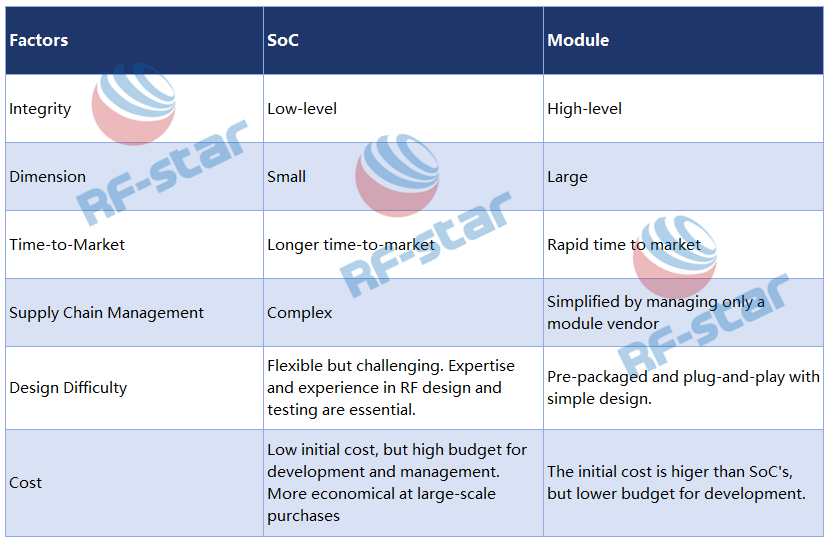
Bluetooth LE-Modul vs. SoC – ein umfassender Vergleich
Basierend auf dem obigen Vergleich sollten Sie bei der Entscheidung zwischen einem Bluetooth- SoC und einem Bluetooth-Modul mehrere Schlüsselfaktoren berücksichtigen :
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass sowohl Bluetooth- SoCs als auch -Module ihre eigenen Stärken und Schwächen haben . Welches ist besser? Das hängt vom jeweiligen Produkt, dem Entwicklungsteam , der Dringlichkeit der Produkteinführung, dem Budget, dem Produktionsvolumen und mehr ab . Wenn Sie während des Entscheidungsprozesses Fragen haben, kann RF-star – ein führender Anbieter von Bluetooth LE- Lösungen mit Modulen und SoCs – Sie hinsichtlich Kosten, Zeitplan und Produktleistung beraten, damit Sie die beste Wahl treffen können.