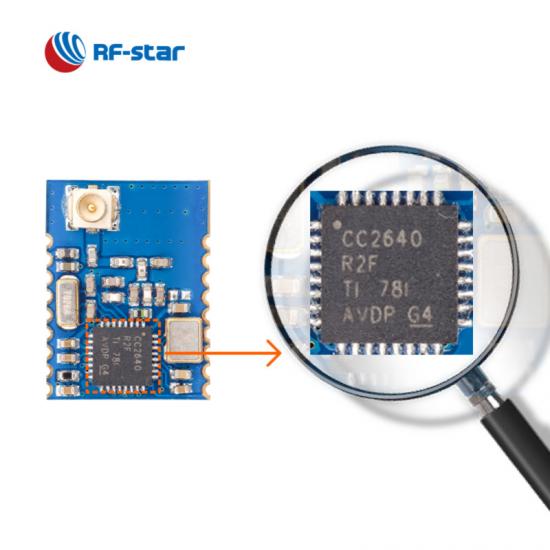
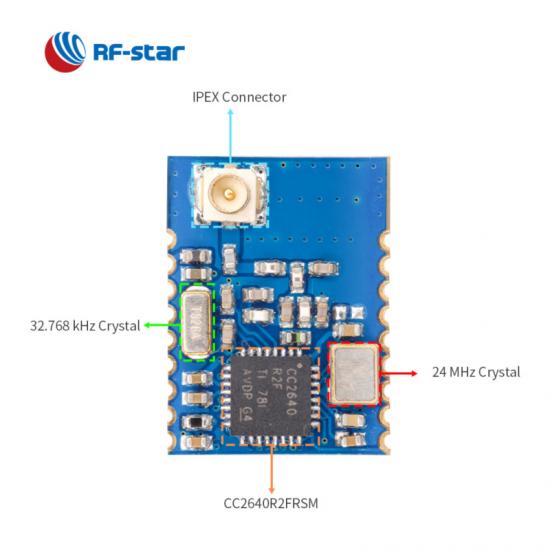
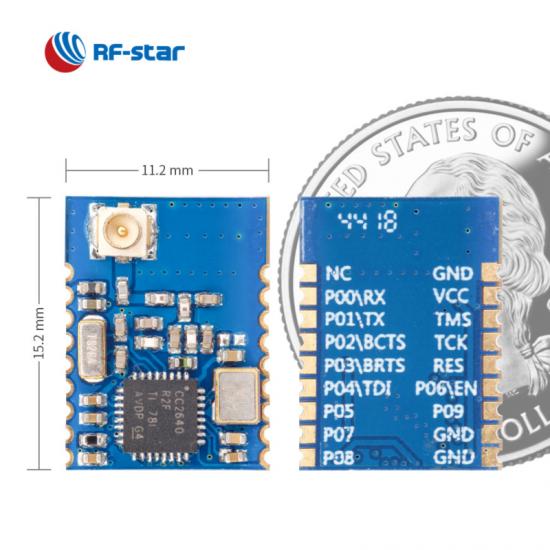
| BLE-Module der Serie CC264x von TI |
| Artikelnummer |
RF-BM-2642B1 |
RF-BM-4077B2 |
RF-BM-4055B1L |
RF-BM-4077B1L |
RF-BM-4077B1 |
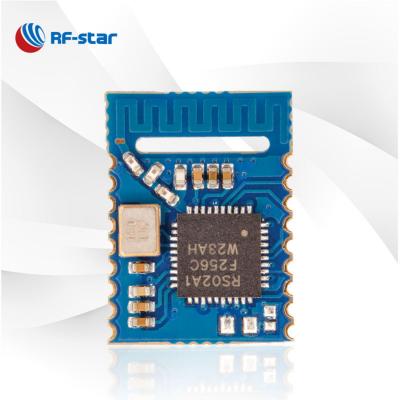
RF-BM-4044B5 |
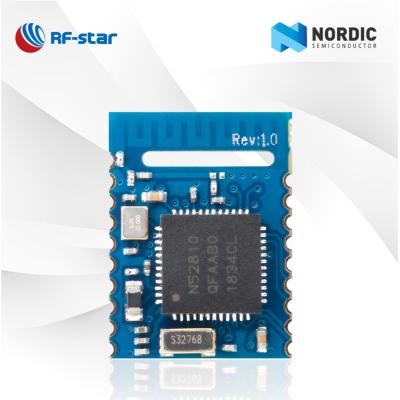
RF-BM-4044B4 |
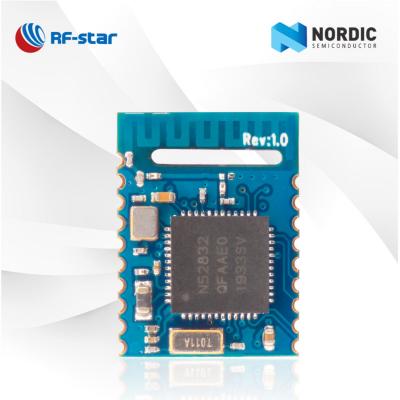
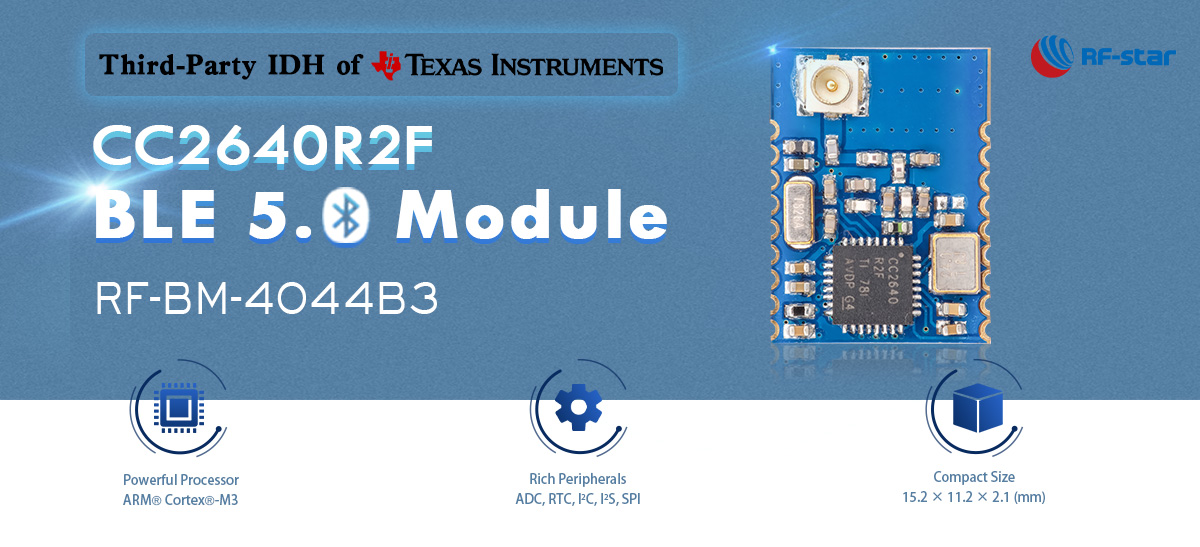
RF-BM-4044B3 |
RF-BM-4044B2 |
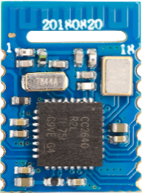
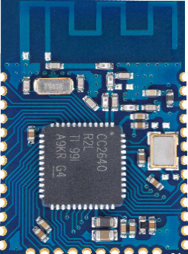
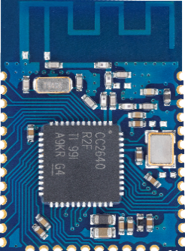
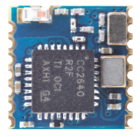
| Foto |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| IC |
CC2642R |
CC2640R2F-Q1 |
CC2640R2LRHB |
CC2640R2LRGZ |
CC2640R2FRGZ |
CC2640R2FRSM |
CC2640R2FRSM |
CC2640R2FRSM |
CC2640R2FRSM |
| Kern |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M4F |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M3 |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M3 |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M3 |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M3 |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M3 |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M3 |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M3 |
48 MHz ARM® Cortex®-M3 |
| Antenne |
Leiterplatte |
Leiterplatte |
Leiterplatte |
Leiterplatte |
Leiterplatte |
Chip/Halbloch-Schnittstelle |
Chip/Halbloch-Schnittstelle |
IPEX |
Leiterplatte |
| RAM |
88 KB |
28 KB |
28 KB |
28 KB |
28 KB |
28 KB |
28 KB |
28 KB |
28 KB |
| Blitz |
352 KB |
128 KB |
128 KB |
128 KB |
128 KB |
128 KB |
128 KB |
128 KB |
128 KB |
| Protokolle |
BLE5.3 |
BLE5.3 |
BLE5.3 |
BLE5.3 |
BLE5.3 |
BLE5.3 |
BLE5.3 |
BLE5.3 |
BLE5.3 |
| Stromversorgung |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
1,8 V ~ 3,8 V, empfohlen bis 3,3 V |
| Frequenz |
2,4 GHz |
2,4 GHz |
2,4 GHz |
2,4 GHz |
2,4 GHz |
2,4 GHz |
2,4 GHz |
2,4 GHz |
2,4 GHz |
| Max. TX-Leistung |
+5 dBm |
+5 dBm |
+5 dBm |
+5 dBm |
+5 dBm |
+2 dBm |
+2 dBm |
+2 dBm |
+2 dBm |
| Empfangsempfindlichkeit |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -105 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -103 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -103 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -103 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -103 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -103 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -103 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -103 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
-97 dBm bei BLE 1M PHY -103 dBm bei 125 kbps LE-codierter PHY |
| GPIO |
31 |
31 |
13 |
31 |
31 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
| Arbeitstemperatur |
-40 ℃ ~ +85 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +105 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +85 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +85 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +85 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +85 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +85 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +85 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +85 ℃ |
| Lagertemperatur |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
-40 ℃ ~ +125 ℃ |
| Übertragungsreichweite |
110 m bei 1M PHY 160 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
100 m bei 1M PHY 150 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
60 m bei 1M PHY, 90 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
70 m bei 1M PHY 100 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
80 m bei 1M PHY 110 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
Chipantenne 30 m bei 1M PHY, 60 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
Chipantenne 20 m bei 1M PHY, 50 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
Externe PCB-Antenne 110 m bei 1M PHY, 150 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
60 m bei 1M PHY, 90 m bei LE-codiertem PHY |
| Abmessung (mm) |
23,5 x 17,0 x 2,2 |
23,5 x 17,0 x 2,2 |
15,2 x 11,2 x 1,7 |
23,5 x 17,0 x 1,7 |
23,5 x 17,0 x 1,7 |
10,5 x 8,5 x 2,0 |
8,0 x 8,0 x 1,5 |
15,2 x 11,2 x 2,1 |
16,6 x 11,2 x 1,7 |
| Paket |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
Halbloch mit 1,27 mm Rastermaß |
| OTA |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
| Bluetooth Mesh |
√ |
× |
× |
× |
× |
× |
× |
× |
× |
| Langstrecken |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
| 2 Mbit/s PHY |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
| AoA/AoD |
√ |
√ |
× |
× |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
| UART-Protokoll |
Master-Slave gleichzeitig |
Meister/Sklave |
Meister/Sklave |
Meister/Sklave |
Meister/Sklave |
Meister/Sklave |
Meister/Sklave |
Meister/Sklave |
Meister/Sklave |
| Funktionen |
Hohe Anti-Interferenz-Leistung |
AEC-Q100-Klasse, hohe Entstörungsleistung |
Hohe Kosteneffizienz |
Hohe Kosteneffizienz |
31 GPIOs für mehr verfügbare Anwendungen |
Kleine Abmessungen, doppelseitige Polster |
Ultrakleine Abmessungen |
Für externe Antennen machbar |
Hohe Stabilität |